 |
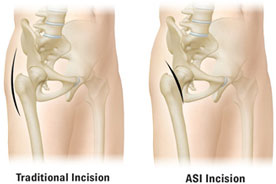 Unlike traditional minimally invasive hip replacement techniques, the ASI technique uses an incision at the front of the hip instead of the side or back of
the hip. This modified incision placement allows surgeons to directly approach the hip joint by going between the muscles that surround the hip joint. Traditional
approaches would require cutting the muscles and/or tendons that surround the hip. The ASI minimally invasive hip replacement procedure is designed to reduce the
trauma to the tissues surrounding the hip joint. By preserving the muscles and tendons, surgeons may enable their patients to walk the day of surgery, to
experience less postoperative pain, and to return to daily activities more quickly.* Unlike traditional minimally invasive hip replacement techniques, the ASI technique uses an incision at the front of the hip instead of the side or back of
the hip. This modified incision placement allows surgeons to directly approach the hip joint by going between the muscles that surround the hip joint. Traditional
approaches would require cutting the muscles and/or tendons that surround the hip. The ASI minimally invasive hip replacement procedure is designed to reduce the
trauma to the tissues surrounding the hip joint. By preserving the muscles and tendons, surgeons may enable their patients to walk the day of surgery, to
experience less postoperative pain, and to return to daily activities more quickly.*
How is the Biomet® ASI Technique Unique?
Biomet worked with leading surgeons to develop unique instrumentation to make the ASI approach reproducible for other surgeons. Similar techniques require a
special, costly operating fracture table. The ASI technique can be performed on either this special fracture table or on a traditional operating room table.
Hundreds of thousands of people undergo total hip replacement every year in the United States. Many patients are not candidates for other minimally invasive
hip surgery techniques due to obesity or other considerations. The ASI technique has the advantage of potentially offering a minimally invasive option for
patients who would not otherwise be considered for other minimally invasive approaches.
Potential Benefits of the ASI Technique are:*
- Shorter hospital stays
- Earlier mobilization
- Accelerated recovery process
- Less blood loss
|
|

- Anterior Supine Intermuscular (ASI) Hip Replacement
- Smaller Incision Hip Surgery
- Conservative Hip Replacement
- Newer Trabecular Metal Cup Backing
- Metal, Ceramic, or Cross-Linked Polyethylene Articulating Surfaces
- Smaller Incision Knee Surgery
- Gender-Specific Knee Replacement
- Partial Knee Replacement (Patellofemoral)
- Partial Knee Resurfacing (Single Compartment)
- Advanced Total Knee Replacement
- Patient Specific Instrumentation Through MRI Navigation
|